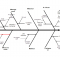
Process mapping using the SIPOC method
Process mapping using the SIPOC method
The SIPOC method explained in Chapter 6.7. At the second team meeting held on July 4, 2012, the author gave a presentation and introduced the team members with the process of recording the process. Afterward, a discussion conducted with a view of the entire process from the analysis indicates, through admission to the Center for Medical Biochemistry, analyzing the delivery of results to the doctor who wrote the laboratory instruction. On that occasion, the SIPOC model was completed and prepared.
Figure 7.10 – Photos from the Lean Project Team meetings 02-2012
| About the organization | ||||||
| Organization | Organization | |||||
| Director | Director | |||||
| Phone | ||||||
| Team leader | Prof.Dr. Vidosava Đorđević | |||||
| Phone | vidadjordjevic@yahoo.com | |||||
| SIPOC process model | ||||||
| Process name | The process of clinical-biochemical laboratory diagnostics at the Clinical Center in Niš | Process designation | A | |||
| Process owner | Dr. sci med Vladan Ćosić | |||||
| Sponsor | Prof.Dr. Borislav Kamenov | |||||
| S | Supplier
|
Clinics of the Clinical Center NisPrimary and secondary health care for Southeast Serbia
Patient on a personal request Scientific research activity; Clinical trials of drugs Central pharmacy KCN Warehouse KCN |
||||
| I | Input | Biological materials: blood, urine, lichen, tissues, punctuates, …Accompanying documentation: ….
Reagents, medical supplies, non-medical consumables. |
||||
| P | Process | A detailed description of the process provided in the continuation of this document. | ||||
| O | Output | Validated results of laboratory analyzesInfectious Waste
Municipal waste Hazardous waste |
||||
| C | Customer | Clinic of the Clinical Center NisDoctors of primary and secondary health care
Patients Health Insurance Fund Pharmaceutical companies |
||||
| Critical resources | A continuous supply of reagents and consumablesSpace for the realization of the process
Admission clinic Spectrophotometer, … LIS – laboratory information system |
|||||
| Feedback | Backlinks with clinicsLosing results sent from the Center for Medical Biochemistry | |||||
| Process parameters | Number of samples received, number of the analyzes performed, number of parameters forged, number of samples collected per hour, the standard duration of analysis, …Number of urgent analyzes | |||||
| The influence of other processes | Supply processDelivery of quality material from the clinic and the ambulance | |||||
Based on the overall process from the analysis to the analysis results, the team members were able to identify and record the macro map of the clinical-biochemical laboratory diagnostics process at the Clinical Center Nis. The process map is in The figure Figure 6.43 – Map of the process of clinical-biochemical laboratory diagnostics.
Team members described in detail all the activities shown in Figure 6.43. Thus, the document “Manual on the Process of Clinical Biochemical Laboratory Diagnostics at the Clinical Center in Nis” was published. This document has 20 pages and gathered knowledge of processes in one place.
The scope of this book does not allow the descriptions of all activities to give, but, for a better understanding, the author has decided to specify a description of only two operations in the process.
Activity A1: Indication of analyzes
Based on a clinical examination and possibly other diagnostic procedures, a specialist from the Clinical Center Nis Clinic is issuing a request to the laboratory for certain types of biochemical analyzes (laboratory instructions). In the laboratory, a patient with a referral and a doctor from primary and secondary health care sent, if they are specialized analyzes that are done only at the tertiary level of health care.
Center for Medical Biochemistry (CMB) for standard biochemical analysis for patients of the Clinic, Clinic Center and functional biochemical analysis for the needs of outpatient and clinical patients.
From the standard analysis, CMB determines substrates (glucose, urea, creatinine, uric acid …), enzymes and isoenzymes (AST, ALT, ALP, γGT, LDH, CK, HBDH, CKMB …), electrolytes and oligo-elements, lipid status, hematological analysis, urine analysis.
The laboratory also performs a specialized analysis:
- Determination of hormones and specific antibodies, blood and urine drugs, specific protein and metabolites related to cardiac (troponin, CKMB mass, BNP, VMA),
- Rheumatic (anti-CCP), hematological diseases (B12, folic acid, transferrin, ferritin, haptoglobin …),
- Immunoglobulins, specific IgE for the group of inhalation and nutritive allergens,
- The laboratory does antibodies for Diagnosis of autoimmune diseases and others.
A list of the most frequent analyzes given in Appendices 1 and 2.
25 Clinics KC Niš for which CMB is working for analysis.
Documents at the entrance to the activity: Laboratory instruction.
Documents at the exit from the activity: Laboratory instruction.
Characteristics/parameters critical quality of laboratory analysis: Adequate selection of analyzes.
Human resources: Doctor KC Niš, primary and secondary care physician.
Activity A2: Sampling of material
IN A RECEIVE AMBULANCE CM. The biological material for patients sent by doctor’s specialists KC Nis and doctors from primary and secondary healthcare activities in Nis and the region conserved. The working hours of the admission clinic are from 7h to 14h every working day. Patients report to the receiving CNT receipt with a health booklet and referral. One of the five laboratory technicians working in the admission clinic CMB takes leaflets and instructions.
According to the laboratory instructions, the first laboratory technician entered into the protocol:
- protocol number;
- general patient;
- type of biological material to be sent;
- The analyses required.
The entire procedure lasts about 40-60s per patient.
- Another laboratory technician bills the services electronically via NexTIS ™, version 6.5.0. The health booklet information loaded with a barcode reader, the entire procedure takes 30-40 s per patient.
- The third laboratory technician opens the laboratory list to which it entered:
- the number from the protocol;
- general;
- type of biological material to be sent;
- the analyses required.
The whole process takes about 60s.
- The same (third) laboratory technician charges participation – the procedure lasts 40-60 s.
- On the required test tubes, the same technician writes the number from the protocol – the procedure takes about 30 s.
- For a general overview of urine, the public data and number of protocols entered by a third technician on a separate sheet.
- The fourth and fifth laboratory technicians call the patient from the waiting room, check in the conversation with him whether all the requirements for adequate preparation of the patient for blood are met (12-hour starvation, a proper collection of 24-hour urine …) – the procedure lasts the 30s.
- One of the two technicians responsible for blood extraction is sampling blood into appropriately labeled tubes – the procedure lasts from 60 to 120 s.
- Sampled tubes are disposed of in the stand and remain there until the laboratory technician receives them (they arrive for the first time around 8:30 and further 2-3 times to 11h).
- The urine brought home from the patient with the accompanying leaflet for the examination of urine is carried to the reception and processing room.
- Exceptionally, in immobile patients, a laboratory technician samples blood on the ground floor (corridor) of the CMB building.